Factory Automation: Transforming Manufacturing with Intelligent and Smart Technologies
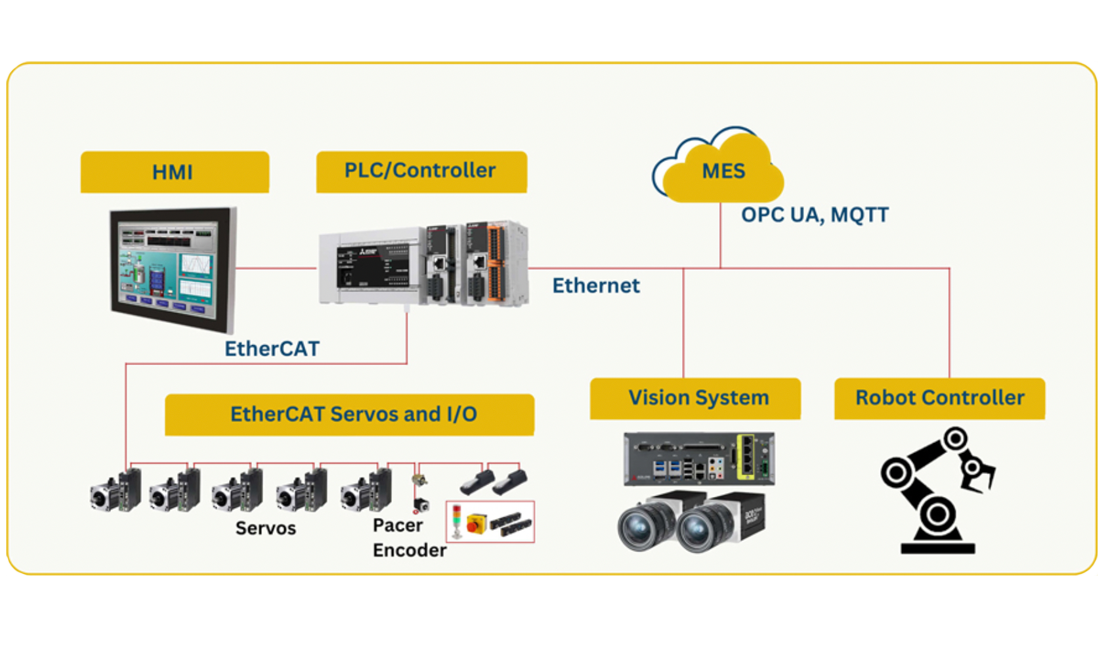
Factory automation refers to the use of advanced technologies, machines, control systems, and software to automate manufacturing processes with minimal human intervention. It plays a crucial role in modern industrial environments by improving productivity, consistency, quality, and operational efficiency. As global competition increases and industries move toward smart manufacturing, factory automation has become a key driver of innovation and growth.
At its core, factory automation involves integrating mechanical systems, electrical components, sensors, controllers, and software to perform tasks such as material handling, assembly, processing, inspection, and packaging. These automated systems are designed to operate continuously, accurately, and safely, reducing dependency on manual labor and minimizing human errors.
Types of Factory Automation
Factory automation can be broadly categorized into three main types: fixed automation, programmable automation, and flexible automation.
Fixed automation is used in high-volume production environments where the product design remains constant. Examples include automotive assembly lines and bottling plants. These systems are highly efficient and cost-effective for mass production but lack flexibility.
Programmable automation allows manufacturers to reprogram machines and systems for different product variations. It is commonly used in batch production, such as CNC machining and industrial robotics, where production requirements may change periodically.
Flexible automation offers the highest level of adaptability. Systems can automatically adjust to produce different products with minimal setup changes. This approach is widely used in smart factories, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands and customization requirements.
Key Components of Factory Automation
Factory automation systems consist of several essential components working together seamlessly. Sensors play a vital role by collecting real-time data related to temperature, pressure, position, speed, and proximity. Actuators, such as motors, valves, and drives, convert control signals into physical actions.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS) serve as the backbone of automation by processing inputs and executing control logic. Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to monitor system performance, visualize data, and control operations efficiently. Industrial communication protocols, such as Ethernet/IP, Modbus, and PROFINET, ensure reliable data exchange between devices and systems.
Role of Robotics in Factory Automation
Industrial robots are a major contributor to factory automation. They are widely used for tasks like welding, painting, assembly, material handling, and palletizing. Robots provide high precision, repeatability, and speed, making them ideal for complex and repetitive operations.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are gaining popularity due to their ability to work safely alongside humans. They are easier to program, cost-effective, and suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises. Cobots enhance productivity while maintaining flexibility and human oversight.
Benefits of Factory Automation
One of the most significant advantages of factory automation is increased productivity. Automated systems can operate 24/7 without fatigue, leading to higher output and faster production cycles. Consistent quality is another major benefit, as automation reduces variability and defects caused by human error.
Factory automation also improves workplace safety by minimizing human exposure to hazardous tasks and environments. It helps reduce operational costs in the long run by lowering labor expenses, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy usage. Additionally, real-time monitoring and data analytics enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending equipment life.
Factory Automation and Industry 4.0
Factory automation is a fundamental pillar of Industry 4.0, which focuses on digital transformation and smart manufacturing. Technologies such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics are transforming traditional automation into intelligent, connected systems.
Smart factories use real-time data to make autonomous decisions, optimize workflows, and improve overall efficiency. Digital twins, cloud platforms, and advanced analytics allow manufacturers to simulate processes, identify bottlenecks, and enhance performance before implementing physical changes.
Challenges in Factory Automation
Despite its benefits, factory automation presents certain challenges. High initial investment costs can be a barrier, especially for small businesses. Integrating new automation systems with existing legacy equipment requires careful planning and technical expertise.
Another challenge is the need for skilled professionals who can design, program, operate, and maintain automated systems. Cybersecurity is also a growing concern, as connected factories are more vulnerable to data breaches and system attacks. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, training, and robust security measures.
Future of Factory Automation
The future of factory automation is driven by continuous advancements in technology. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable more adaptive and self-optimizing systems. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) will enhance logistics and material movement within factories. Edge computing will support faster decision-making by processing data closer to the source.
Sustainability will also play a key role, with automation helping manufacturers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and meet environmental regulations. As factories become smarter and more connected, automation will continue to redefine manufacturing efficiency and competitiveness.
Conclusion
Factory automation is transforming the manufacturing landscape by enabling faster, safer, and more efficient production processes. Through the integration of advanced technologies, robotics, and intelligent control systems, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, improved quality, and greater flexibility. As industries move toward smart factories and Industry 4.0, factory automation will remain a critical factor in driving innovation, sustainability, and long-term industrial success.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



