Enhancing Business Resilience Through Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
Introduction to Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a structured and holistic approach used by organizations to identify, assess, manage, and monitor risks. It encompasses all types of risks—strategic, operational, financial, and compliance-related—to ensure that decision-making processes align with the organization’s goals and risk appetite.
Unlike traditional risk management that operates in silos, ERM is integrated across departments and functions. It enables companies to proactively address potential threats and opportunities, ultimately improving business performance and sustainability.
Core Components of ERM
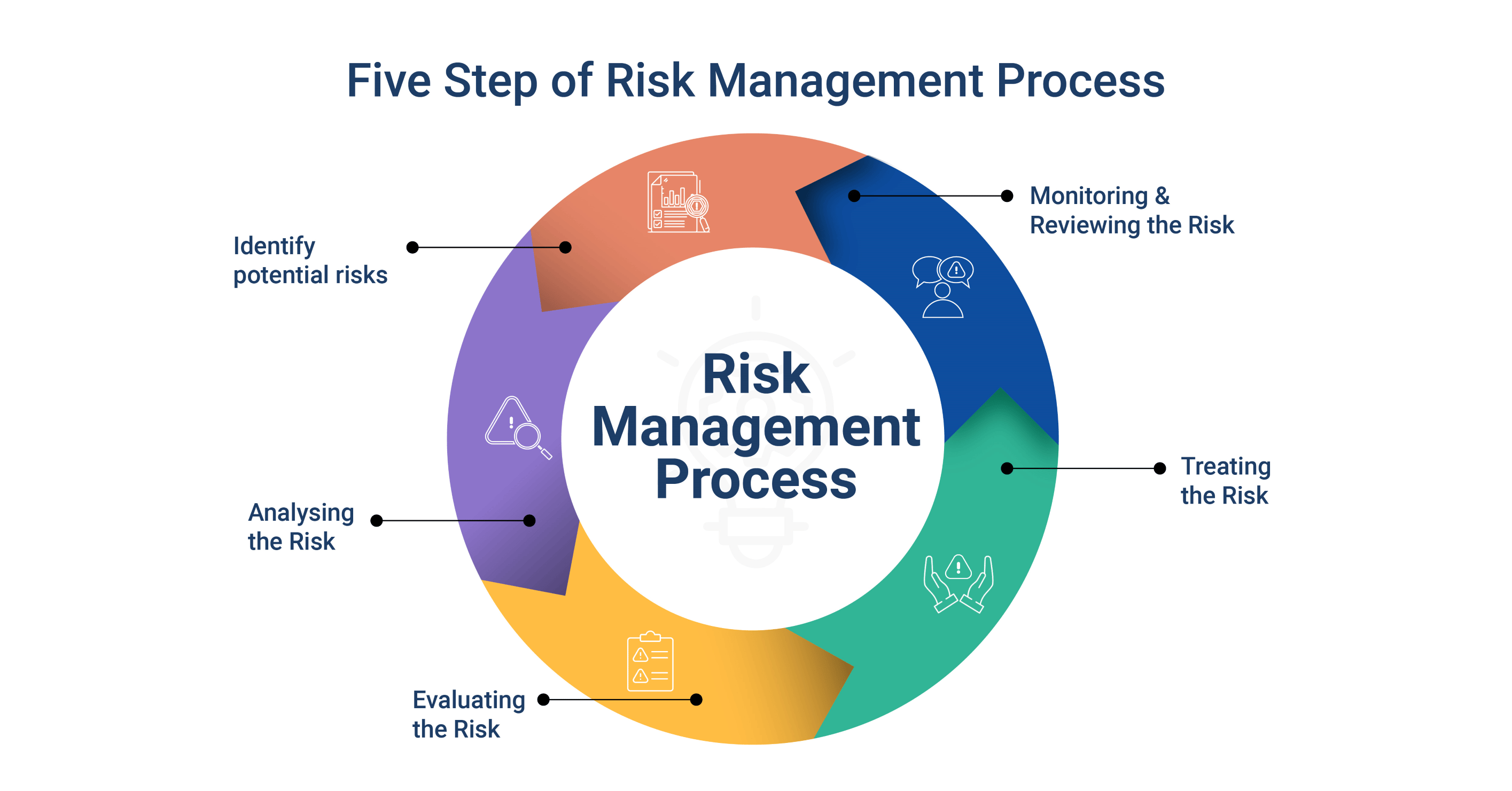
At the heart of ERM are several critical components, including risk identification, risk assessment, risk response, and monitoring. These elements work in a continuous cycle, ensuring that organizations can adapt to emerging threats and shifting market conditions.
Risk identification focuses on uncovering both internal and external factors that could impact objectives. Assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and impact of each risk, while response strategies can include avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance. Monitoring ensures that these strategies are effective and updated as needed.
Benefits of Implementing ERM
ERM provides a comprehensive view of organizational risks, promoting informed decision-making and better resource allocation. This helps businesses prioritize risks based on severity and likelihood, allowing them to focus on what truly matters.
Moreover, ERM fosters a culture of transparency and accountability. It enhances communication across all levels of the organization, enabling leaders and employees to understand how their actions influence overall risk exposure.
Strategic Alignment Through ERM
One of the key advantages of ERM is its ability to align risk management with strategic planning. By embedding risk considerations into strategic initiatives, companies can make more resilient and flexible business plans.
ERM encourages organizations to think ahead and incorporate risk scenarios into long-term goals. This strategic foresight supports sustainability and competitive advantage by enabling organizations to adapt quickly to uncertainty.
ERM and Regulatory Compliance
In today’s complex regulatory landscape, ERM plays a crucial role in maintaining compliance and avoiding legal pitfalls. By systematically addressing compliance risks, ERM helps businesses meet regulatory standards and prepare for audits.
Regulators and stakeholders increasingly demand evidence of sound risk management practices. A robust ERM framework can provide this assurance and reduce the likelihood of penalties or reputational damage.
Technology and ERM Integration
The rise of digital transformation has significantly enhanced the capabilities of ERM systems. Modern ERM solutions leverage data analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation to provide real-time insights and risk predictions.
These technological advancements allow companies to track key risk indicators (KRIs) more accurately. With dashboards and predictive models, decision-makers can proactively manage risks before they escalate into crises.
ERM in Crisis Management and Business Continuity
ERM is vital for preparing organizations for unexpected disruptions, such as economic downturns, cyberattacks, or natural disasters. By incorporating crisis response and business continuity into the ERM framework, companies can maintain operations during emergencies.
Preparedness plans developed under ERM help organizations respond swiftly, minimizing financial and reputational losses. These proactive strategies strengthen resilience and boost stakeholder confidence.
Building a Risk-Aware Culture
Successful ERM implementation depends heavily on organizational culture. A risk-aware culture encourages employees to recognize, report, and address risks without fear of blame. This promotes continuous improvement and safeguards against future issues.
Training, leadership support, and clear communication are essential for embedding risk awareness throughout the organization. When everyone understands their role in risk management, the business becomes more agile and responsive.
Challenges in ERM Adoption
Despite its benefits, ERM implementation can face several obstacles, including resistance to change, lack of awareness, or insufficient resources. Many organizations struggle to move beyond a checklist approach and integrate ERM meaningfully into daily operations.
To overcome these challenges, leadership commitment and tailored strategies are critical. Customizing ERM frameworks to suit organizational size, industry, and maturity ensures long-term success.
Source - https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/enterprise-risk-management-market-20681
As businesses face increasingly complex risks, the importance of Enterprise Risk Management continues to grow. ERM is not just a protective measure—it is a strategic enabler that supports innovation, stability, and growth.
By embedding ERM into their DNA, organizations can better navigate uncertainty, build stakeholder trust, and achieve long-term value. In an ever-changing world, ERM is a vital tool for building resilient, adaptive, and successful enterprises.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Oyunlar
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



