The AI Assembly Line: Deconstructing the Data Annotation And Labelling Market Platform
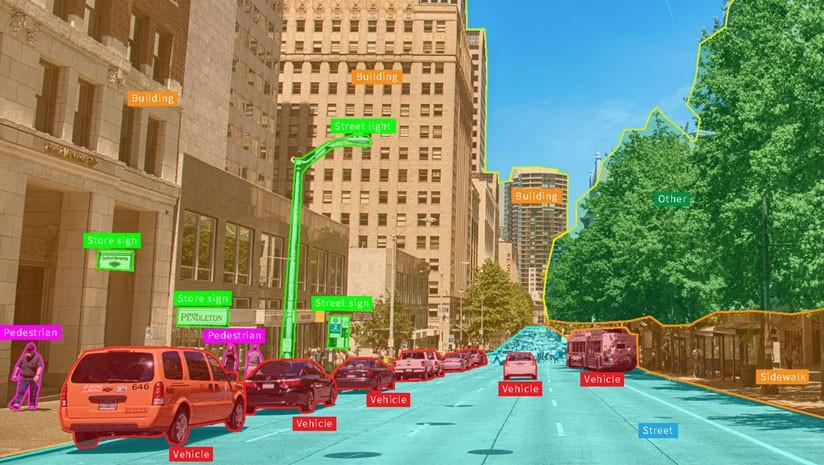
The process of labeling millions of data points requires more than just a simple drawing tool; it requires a sophisticated and highly engineered software system. A modern Data Annotation And Labelling Market Platform is an end-to-end "AI assembly line," a comprehensive platform designed to manage the entire data annotation lifecycle, from data ingestion and task distribution to quality control and final export. The architecture of such a platform can be broken down into three core layers: the annotation interface (the workbench), the workflow and project management engine, and the quality assurance and analytics layer. The first and most user-facing layer is the annotation workbench. This is the interactive interface where the human annotators perform the actual labeling tasks. A leading platform will offer a suite of specialized tools tailored to different data types and annotation tasks. For images, this includes intuitive tools for drawing precise bounding boxes, polygons, and keypoints, as well as "smart" brush and segmentation tools that can make pixel-level annotation faster and easier. For text and audio, it provides interfaces for highlighting entities, applying sentiment tags, or transcribing speech. The efficiency, responsiveness, and user-friendliness of this workbench are critical, as they directly impact annotator productivity and the overall cost of a project.
The second architectural layer, operating behind the scenes, is the workflow and project management engine. This is the "brain" of the platform, responsible for orchestrating the entire annotation process at scale. This layer handles the ingestion of raw data and its distribution to the workforce. A project manager can use this engine to define the specific instructions for a labeling task, set up the project, and assign it to a team of annotators. A key feature is the ability to create complex, multi-stage workflows. For example, a common workflow involves having an initial annotation performed by one person, which is then sent to a second, more senior person for review and correction. The platform can even implement a "consensus" model, where the same data point is labeled by multiple annotators, and the platform automatically flags any disagreements for a final review. This workflow engine is what allows a project manager to efficiently manage a team of hundreds or even thousands of distributed annotators while maintaining control over the entire process, a crucial capability for large-scale projects.
The third and arguably most important layer is the quality assurance (QA) and analytics layer. The old adage "garbage in, garbage out" is the fundamental truth of machine learning; the quality of the labeled data directly determines the performance of the AI model. This layer provides the tools to ensure and measure that quality. It includes features for automatically tracking key quality metrics, such as the agreement rate between different annotators or the number of corrections made during the review process. It provides dashboards that allow project managers to monitor the performance of individual annotators, identify those who may need additional training, and reward top performers. This layer often incorporates a concept known as "human-in-the-loop" (HITL) or "active learning." The platform can use the AI model that is being trained to automatically flag data points that the model is least confident about. These "edge cases" are then prioritized and sent back to human annotators for review, creating a virtuous cycle where human and machine work together to continuously improve both the dataset and the model itself.
Finally, a modern platform is built with robust security and seamless integration in mind. Given that these platforms often handle sensitive or proprietary data—from medical images to pre-release product designs—security is paramount. The platform's architecture must include features like role-based access control, end-to-end data encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. The integration capabilities are equally critical. A leading platform will offer a rich set of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow it to be easily integrated into a company's broader MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) pipeline. This allows for the automated ingestion of data from cloud storage (like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage) and the seamless export of the finished, labeled datasets directly into the AI model training environment. This API-first approach ensures that the annotation platform is not an isolated silo but a deeply integrated and automated component of the end-to-end AI development process.
Top Trending Reports:
Fraud Detection and Prevention Market
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Παιχνίδια
- Gardening
- Health
- Κεντρική Σελίδα
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- άλλο
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



